PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY
Our company will provide you with:
- defining a group of producers that meet your requirements,,
- selection of the best producers,
- organization of meetings with potential suppliers,
- translator and guide service,
- reservation of air and rail tickets,
- accommodate you in hotels,
- car rental.
Below we present our sample analyzes related to the pharmaceutical industry. They concern the market situation in the world and in Poland. We also encourage you to familiarize yourself with the offer tailored specifically to customers from the pharmaceutical industry.
World pharmaceutical industry
Medicine is a field whose services will always be in demand. Due to the growing life expectancy, the demand for medicines that are necessary for the elderly will increase. However, younger people, especially from the middle class, buy various pharmaceuticals not only in the moment of illness, but also to counteract it or improve the condition of their body.
Experts expect the value of the global pharmaceutical market to grow to almost USD 1.6 trillion in 2020. The PwC report indicates that the largest increase will occur in emerging market countries, where sales will more than double from USD 205 billion in 2011 to 499 USD billion in 2020. The result is not surprising, as this group includes such large markets as all the BRICS countries and incl. Poland. Big growth is also expected in the US market (from USD 337 to 425 billion). A slight decrease will occur only in the group of 5 “old Europe” countries (France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Great Britain).
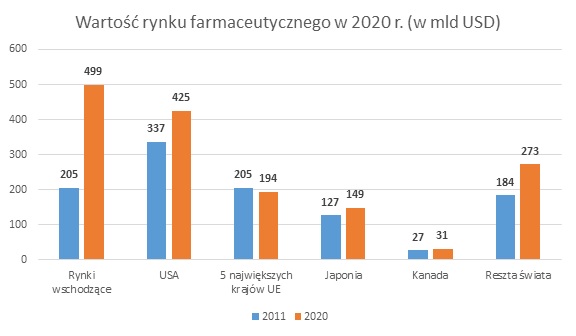
Source: http://www.pwc.com/gx/en/pharma-life-sciences/pharma2020/market-opportunities-and-outlook.jhtml
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most innovative branches of the economy. Companies spend significant sums on research and development – in the United States alone, entities belonging to PhRMA (Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America), an association associating industry entities, allocated approximately USD 51.1 billion for this purpose in 2013. In 2012, this amount amounted to USD 49.6 billion, and a year earlier – USD 48.6 billion. In the 21st century, PhRMA members created 400 new drugs, and another as many are under development.
In Europe, the pharmaceutical industry is also of great economic importance. In 2013, R&D expenditure in this area exceeded EUR 30.6 billion. The largest outlays are made in Germany (EUR 5.8 billion in 2012), Great Britain (EUR 5.1 billion in 2012) and Switzerland (EUR 5 billion in 2007). The production value this year was EUR 217.5 billion. Brazil, China and India are becoming increasingly important markets, with a double-digit increase in value in 2013 (Brazil – 17%, China – 14%), while the top 5 European countries 1%, and the USA – 3%.
The United States remains the leader in the pharmaceutical industry. In terms of the value of drug sales, North America accounts for 41% of the total, and Europe for 27.4%. More than half (55%) of new drugs are introduced for the first time on the US market, and 23% in Europe.
It takes several years to create a drug from the moment a substance is created to its introduction to the market. The total cost of the trial in 2012 was estimated at $ 1.5 billion. Only 1-2 out of 10,000 tested substances go through the entire path that ends with a successful marketing.
The industry in question is characterized by the highest added value per one employed person among all high technology industries. Moreover, it has the highest ratio of R&D investment to income. Expenditure on R&D in pharmaceutical and biotechnology account for 18.1% of all expenditure for this purpose in the global economy. Due to the necessity to incur large expenditures, the industry tends to concentrate – it is easier for larger entities to obtain the necessary funds.
Due to patient safety, the pharmaceutical market is regulated by appropriate institutions. These rules differ depending on the country, which results in different prices, forms of promotion, registration procedure, etc. This is one of the reasons for importing drugs from countries where they are cheaper, i.e. parallel import. In Europe, the main importers by this route are Great Britain and Denmark. In 2010, the value of parallel imports in Europe was estimated at EUR 4.3 billion.

